
Every person is unique!
Our experienced team will be happy to advise you in detail and free of charge on all matters relating to your health. Book your consultation appointment now:
Protect against dementia - treat dementia
October 13, 2022
Dr. Dorothee Bös et al.
Dementia can affect any of us. In addition to age, various other factors increase the probability of contracting the disease. There is no therapy so far. Learn here how you can lower the risk of dementia with the help of vital mushrooms and improve your general health at the same time. Even people who are already ill can improve their quality of life by using suitable medicinal mushrooms.
What is dementia?
 Most people associate dementia with pronounced forgetfulness. Depending on the type of dementia, however, the focus is also on the decline of other brain functions. That is why the term “dementia” generally encompasses all diseases that are associated with declining mental abilities.
Most people associate dementia with pronounced forgetfulness. Depending on the type of dementia, however, the focus is also on the decline of other brain functions. That is why the term “dementia” generally encompasses all diseases that are associated with declining mental abilities. Who is affected by dementia?
Across Europe, 8.5% of the 65+ population is affected by dementia. Women (10 %) are significantly more likely to develop the disease than men (6 %). Next to gender, age is the biggest risk factor. For example, of those aged 75-79, about 7.6% suffer from declining brain function, compared to over one-third of Europeans aged 90+.
What are the different forms of dementia?
The different forms of dementia can be assigned to the two groups “primary dementia” and “secondary dementia”. In primary dementias, there is no known cause or the brain’s degradation process itself is the reason for the declining cognitive abilities. In secondary dementias, on the other hand, there is another underlying disease that leads to the degradation processes in the brain.
Alzheimer
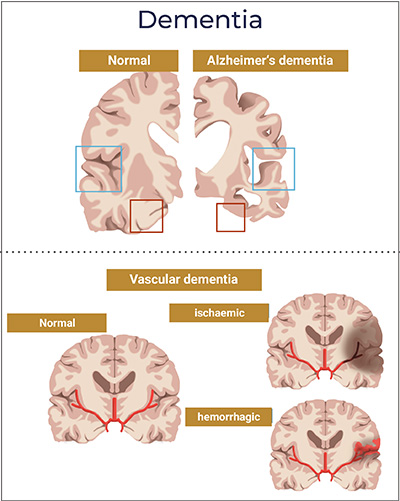
With about 60% of all dementia cases, Alzheimer’s disease ranks first among the forms of dementia. The terms “dementia” and “Alzheimer’s disease” are therefore often used synonymously, but this is not scientifically correct.
To date, the exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are unknown. Therefore, there is no therapy for this form of dementia. The only thing that is now known is that an increased number of small fragments of the so-called tauprotein, the tau fibrils, are deposited in the brain of those affected. They lead to the death of brain cells and thus to a decrease in brain mass. In addition, there are so-called “amyloid plaques”. These are protein deposits between the nerve cells in the brain. Where these plaques come from and why they do not lead to Alzheimer’s in everyone is as yet unclear.
If you want to prevent this form of dementia, you should focus on some risk factors, which we present below.

Every person is unique!
Our experienced team will be happy to advise you in detail and free of charge on all matters relating to your health.
Vascular dementia
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia (10-15%). Mixed forms with Alzheimer’s disease often occur. In vascular dementia, the reason for the degeneration of the brain is a circulatory disorder. Here, the specific memory loss is usually less noticeable than a general slowing of thinking in combination with severe mood swings.
Various risk factors are known for the circulatory disorder. A major one is high blood pressure. It causes wall thickening and eventual occlusion in the smallest blood vessels in the brain. “Mini infarcts” occur, from which the surrounding nerves suffer damage. The other risk factors are similar to those of atherosclerosis: obesity, elevated cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease. With vital mushrooms you can prevent vascular dementia, as they counteract the above risks.
Lewy body
 However, in dementia with Lewy bodies, the dementia degradation process is the main focus. Symptoms typical of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremor or stiffness, tend to occur on the periphery and, if so, only in the later course of the disease. Initially, strong fluctuations in thinking performance as well as attention are noticeable. Visual hallucinations occur. Affected individuals tend to fall and lose consciousness. Another symptom is uninhibited movements during the dream phase.
However, in dementia with Lewy bodies, the dementia degradation process is the main focus. Symptoms typical of Parkinson’s disease, such as tremor or stiffness, tend to occur on the periphery and, if so, only in the later course of the disease. Initially, strong fluctuations in thinking performance as well as attention are noticeable. Visual hallucinations occur. Affected individuals tend to fall and lose consciousness. Another symptom is uninhibited movements during the dream phase. Rare and secondary forms of dementia
A final but very rare primary form of dementia is fronto-temporal dementia. It affects about 5% of all dementia patients. In this disease, the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain shrink. As a result, there is a change in the nature and emotions of those affected. On average, these are younger than the average Alzheimer’s patient. In a late stage of the disease, memory problems may also occur. Little is known about the causes of fronto-temporal dementia.
Secondary dementia can occur as a result of these diseases:
- Craniocerebral injuries
- Brain tumors
- Parkinson’s disease -> Dementia occurs in around a third of people in the late stages of the disease.
- Hypothyroidism
- Chronic alcoholism or encephalitis can lead to Korsakov’s syndrome. In this dementia, new information is no longer stored.
- Inflammatory diseases of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis
Here, dementia therapy must always take into account the primary disease. Vital mushrooms can then be selected according to the underlying diseases or with the goal of a higher quality of life.
How can I recognize dementia?
Since it is impossible to cure dementia, early detection is all the more important. The sooner a neurologist makes the diagnosis, the better the course can be influenced. But how do you recognize the onset of dementia? A typical sign, especially in Alzheimer’s disease, is increasing forgetfulness. In addition, look for the following signs:
- In new surroundings, orientation is more difficult than usual.
- The sense of time diminishes.
- Mood fluctuates more than before. [2]
- Learning new things requires much more effort.
- Words no longer come to mind.
- Situations are repeatedly misjudged.
Depending on the type of dementia, other symptoms are in the foreground. Especially in the later course of the disease, depressive moods and sleep disturbances often impair the quality of life. Here, balancing vital mushrooms such as the Reishi can provide relief.
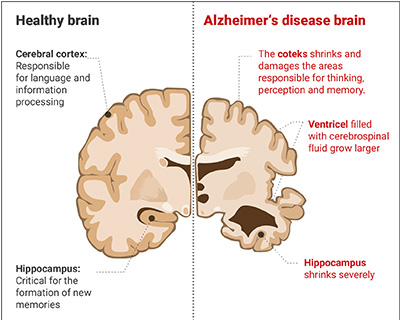
How does Alzheimer's develop?
In the following look at the development of dementia, we will focus on Alzheimer’s disease, as it is the most widespread form. We will point out overlaps with other types of dementia as appropriate.
Basically, little is known about the causes of dementia. Only in 2% of Alzheimer’s patients, as well as in a proportion of those affected with Lewy bodies, is a genetic condition established. This means that a particular gene variant is the sole cause of the disease. In addition, there is still a genetic predisposition that increases the likelihood of Alzheimer’s, but does not necessarily lead to the disease.
Risk factors obesity and diabetes
This point is as relevant to Vascular Dementia as it is to Alzheimer’s! Indeed, obesity and diabetes are closely related to hypertension and arteriosclerosis, the causes of vascular dementia.
Dementia has increased dramatically in recent decades. This is often justified by a generally higher life expectancy, but this is not true. In fact, the prevalence of Alzheimer’s increased not in parallel with life expectancy, but with factors that we can summarize under “Western diet and lifestyle.” These include, first and foremost, a lack of exercise and an unfavorable diet. In addition to insufficient nutrient intake, this is characterized by an unfavorable composition of fatty acids and an excessive intake of animal proteins as well as sugar. As a result of this unfavorable lifestyle, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, abdominal obesity and diabetes occur more frequently.
 Alzheimer’s patients have been found to have increased numbers of nerve cells with deposits of saccharified proteins. Some of these “candied” protein structures come directly from fast food and similarly unhealthy foods. However, the body also produces them itself when, for example, the blood sugar level is too high in a diabetic. In addition to being deposited in brain cells, the saccharified proteins damage certain structures, such as the walls of blood vessels. This in turn increases the risk of arteriosclerosis.
Alzheimer’s patients have been found to have increased numbers of nerve cells with deposits of saccharified proteins. Some of these “candied” protein structures come directly from fast food and similarly unhealthy foods. However, the body also produces them itself when, for example, the blood sugar level is too high in a diabetic. In addition to being deposited in brain cells, the saccharified proteins damage certain structures, such as the walls of blood vessels. This in turn increases the risk of arteriosclerosis.
If you want to prevent dementia, a healthy diet with high-fiber foods such as whole grains, vegetables, mushrooms, salads and fruits is essential. Optimally, you consume them raw or only steamed, because high-fat foods and fried foods are also problematic for health. To counteract abdominal obesity and diabetes, the vital mushrooms Coprinus and Maitake are also recommended, which can favorably influence the sugar and fat metabolism, increase satiety and support a healthy body weight. With the help of medicinal mushrooms can also counteract the saccharification!
Risk factor environmental toxins
 Elevated levels of pesticides and aluminum have been found in brains of some Alzheimer’s patients. Aluminum is a severe neurotoxin and comes from many sources these days. It can lead to the death of nerve cells. However, aluminum is not the only problem. In general, we are dealing with numerous environmental toxins today and should therefore support our detoxification organs liver and kidney permanently. From the mushroom side, Cordyceps is suitable for kidney health and Reishi for the liver.
Elevated levels of pesticides and aluminum have been found in brains of some Alzheimer’s patients. Aluminum is a severe neurotoxin and comes from many sources these days. It can lead to the death of nerve cells. However, aluminum is not the only problem. In general, we are dealing with numerous environmental toxins today and should therefore support our detoxification organs liver and kidney permanently. From the mushroom side, Cordyceps is suitable for kidney health and Reishi for the liver.
Ideally, one should generally consume food that is as uncontaminated as possible. Those who want to prevent dementia should therefore mainly use wholesome regional organic foods. Fatty sea fish should be avoided, as it often contains the toxic methylmercury. A good acid-base balance and a healthy mineral intake are also helpful – this can make it more difficult to store heavy metals. Mushrooms, as alkaline foods, promote a healthy acid-alkaline balance. They are also rich in vitamins and minerals.
Risk factor oxidative stress
Oxidative stress plays an important role not only in Alzheimer’s disease, but also in all other types of dementia. Due to sugared proteins, trans fats and heavy metals, but also due to inflammation, so-called oxidative stress occurs in the body. This means that free radicals are not sufficiently scavenged by antioxidants. The central nervous system (i.e. also the brain) reacts very sensitively to oxidative stress. Permanent damage can occur here. Vital mushrooms are very rich in antioxidants.
One of the most important antioxidants in the brain is glutathione. Mushrooms have the ability to directly stimulate the formation of glutathione in the body. In addition, mushrooms contain the nerve-protective amino acid ergothione, which is a kind of super antioxidant that can accumulate in the nervous system and thus provide maximum protection. Hericium is rich in this anti-aging substance.
Risk factor poor circulation and lack of oxygen
 With all forms of dementia, it is important to address vascular conditions such as hypertension early on. Improving the circulation situation is essential, as dementia patients often have damaged blood vessels, arteriosclerosis, microstrokes and inflammatory processes. Medicinal mushrooms such as Auricularia, Cordyceps, Reishi and Shiitake are particularly suitable for this purpose.
With all forms of dementia, it is important to address vascular conditions such as hypertension early on. Improving the circulation situation is essential, as dementia patients often have damaged blood vessels, arteriosclerosis, microstrokes and inflammatory processes. Medicinal mushrooms such as Auricularia, Cordyceps, Reishi and Shiitake are particularly suitable for this purpose.
In addition, Reishi can positively influence blood oxygen levels and help protect blood vessels. Auricularia, in turn, ensures good blood circulation and counteracts clots. In addition, protective effects of vital mushrooms on healthy tissue have been observed in the case of oxygen deficiency, such as occurs in infarctions.
How can dementia be treated?

Unfortunately, a true dementia therapy is not yet known. Only palliative medications are available to slow the progression. In secondary dementias, the focus is also on treating the underlying disease. As can be seen from the various risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and, to some extent, other forms of dementia, prevention offers the only possible protection against a degenerative brain disease. With the help of a healthy lifestyle, carefully selected foods and the appropriate medicinal mushrooms, some other health factors can also be influenced. In this way, it is also possible to decisively improve the quality of life of dementia patients.
Regenerate neurons with vital mushrooms
At this point we would like to introduce you to the effect of two particularly important medicinal mushrooms in connection with dementia: Reishi and Hericium.
 They cannot cure dementia, but they have very promising properties in terms of preventing and slowing the disease. Indeed, both mushrooms can support the regeneration of nerves. With their ingredients, they increase BDNF (brain derived neurotropic factor) and NGF (nerve growth factor) levels. Both are central to the protection of neurons as well as synapses and are also involved in the development of nerve cells.
They cannot cure dementia, but they have very promising properties in terms of preventing and slowing the disease. Indeed, both mushrooms can support the regeneration of nerves. With their ingredients, they increase BDNF (brain derived neurotropic factor) and NGF (nerve growth factor) levels. Both are central to the protection of neurons as well as synapses and are also involved in the development of nerve cells.
Overview of other helpful vital mushrooms for dementia
- Auricularia: stimulates blood circulation, anti-arteriosclerotic, lowers cholesterol, improves oxygen and nutrient supply to the cells and the removal of “cellular waste”.
- Shiitake: cholesterol-lowering, prevents arteriosclerosis, anti-inflammatory, liver-protective
- Coprinus: positively influences sugar and fat metabolism
- Cordyceps: detoxifying (kidney), regulates blood sugar, stimulates blood circulation
- Pleurotus: rich in vitamins, prebiotic, cholesterol-lowering.
Meanwhile, there are numerous studies regarding the mode of action of mushrooms in dementia. The change of the intestinal flora favors the formation of nerve-protective short-chain fatty acids, the spermidine of the mushrooms supports healthy cell cleansing (autophagy) and the antiviral properties of the mushrooms are used against the possible dementia risk factor herpes.
In a double-blind study, seniors with the onset of dementia took Hericium mushroom powder for 4 months, which significantly improved symptoms. However, it worsened again after stopping the Hericium; so I guess you have to take it much longer.
Other studies also suggest that vital mushrooms are probably most effective in the early stages of the disease. The extent to which vital mushrooms can be used to treat dementia that is already more advanced has not yet been adequately studied.
Buy vital mushrooms
 If you want to treat or prevent dementia with vital mushrooms, please get comprehensive advice! Our experts are available to assist you with their in-depth knowledge free of charge. After that, be sure to pay attention to the following quality criteria when choosing a mushroom supplier:
If you want to treat or prevent dementia with vital mushrooms, please get comprehensive advice! Our experts are available to assist you with their in-depth knowledge free of charge. After that, be sure to pay attention to the following quality criteria when choosing a mushroom supplier:
- Mushroom powder from the whole mushroom
- gentle drying at below 40° Celsius
- Compliance with German organic guidelines for mushroom cultivation
- Filling the mushroom powder into capsules
If all these criteria are met, you can be sure that the vital mushrooms really support your health. With all other providers, you do not know whether all the important ingredients are actually contained, but no harmful substances.
DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS?
We will gladly take time for you. In our free consultation we answer individually and personally all your health questions under:
